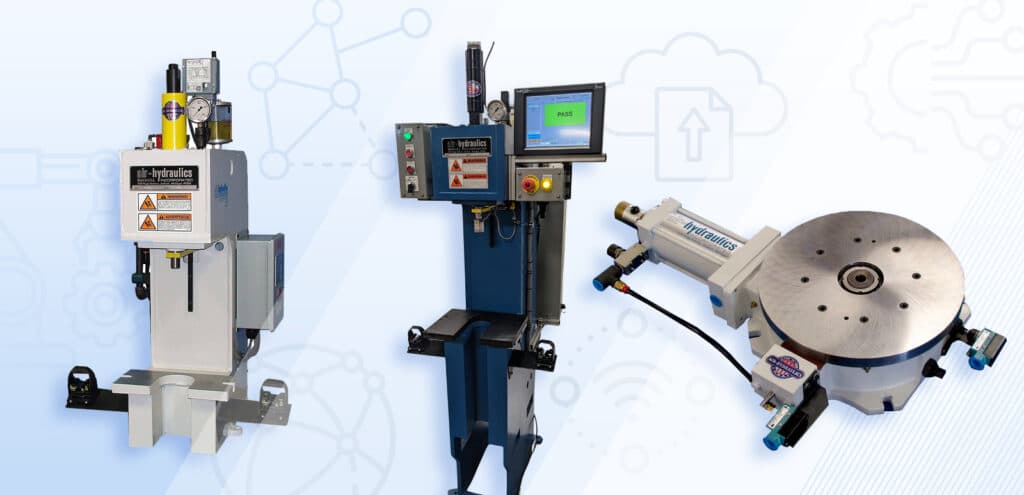
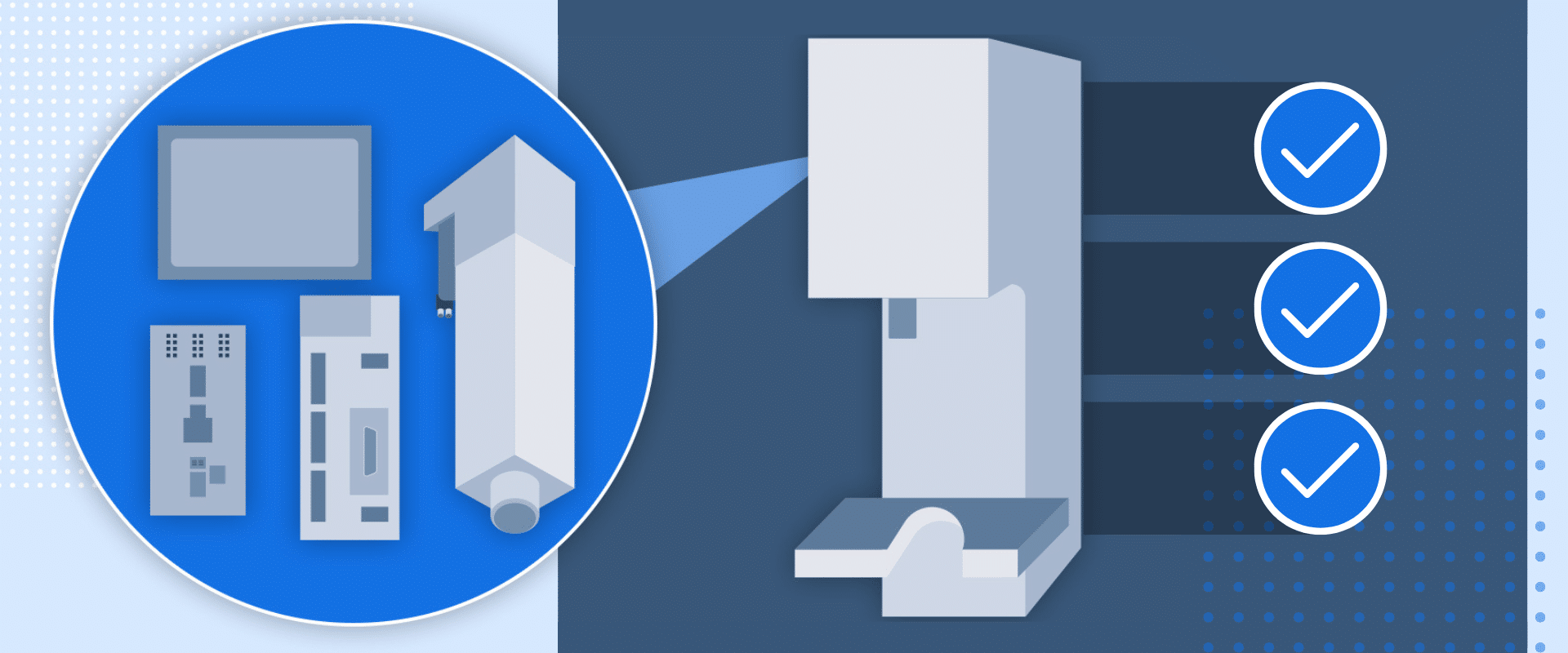
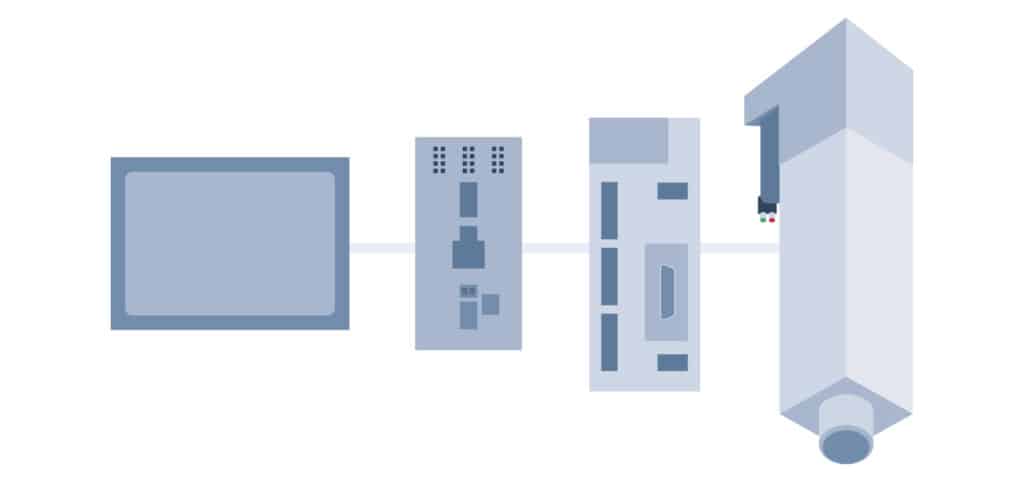
Press monitoring systems have helped to substantially improve press performance across nearly any industry. Once optional add-ons, these monitoring systems are quickly becoming must-haves for many applications. However, choosing the best monitoring system upgrades can be difficult. Let’s take a look at different press monitoring equipment options and different applications they might be ideal for.
What is Press Monitoring Equipment?
First, what is press monitoring equipment? Press monitoring equipment consists of sensors and control systems that collect real-time data from a press during its operation. This data can include information such as force, position, displacement, cycle timing, and pressure. These mechanisms use this data to ensure each cycle meets set parameters, identify potential problems early, and confirm the quality of every assembled part.
By installing the right monitoring system, manufacturers can move away from costly manual inspections, reduce the risk of defective parts reaching customers, and extend the life of their equipment by preventing overloading or improper operation.
Types of Press Monitoring Systems
Choosing the right press monitoring equipment starts with understanding the different types of systems available. Each type offers distinct advantages depending on your process requirements.
Basic Force Monitors
For many straightforward applications, a basic force monitoring system provides a cost-effective solution. Force monitors measure the force applied during the press cycle and compare it against predefined limits. If the press applies too little or too much force—potentially indicating a missing component or material issue—the system provides a “failed” feedback report, or in some cases triggers an alarm, stops the cycle, or prohibits the press from cycling without acknowledgement from an operator.
Force monitors are ideal for relatively simple assemblies where force measurement alone is an accurate determining factor for quality. They offer quick feedback with minimal setup, and can even be added onto an existing press, making them perfect for basic manufacturing tasks or lower-risk products.
Force and Distance Monitoring Systems
More complex assemblies often require additional control over the position of the press ram as well as the force being applied. Force and distance monitoring systems track both metrics throughout the press stroke. Instead of simply checking peak force, these systems ensure that the press follows an exact force-and-distance path during each cycle.
This type of monitoring is especially valuable in applications with tight tolerances, such as automotive components, electronics, and medical devices. Being able to confirm that both the force and position meet exact parameters at every stage of the press stroke greatly improves process repeatability and product quality.
Take a look at force and distance monitoring press equipment >
Digital Process Signature Analysis Systems
Digital process signature analysis systems provide even more detailed data analysis than force and distance monitoring. These systems record the entire press cycle using various data points, such as force, pressure, distance, torque, and more. The system then uses this data to compile a “signature;” a visual presentation of the process. The machine can then compare this to a known signature which meets key requirements. Small deviations from the ideal curve can be used to detect issues such as material defects, improper part positioning, or mechanical problems with the press itself.
Signature analysis is especially useful in high-volume manufacturing where small mistakes can lead to major rework costs if undetected. By spotting subtle variations early, signature monitoring allows manufacturers to fine-tune processes, reduce scrap, and prevent faulty parts from reaching the next stage of production.
Integrated Monitoring in Servo Presses
Modern servo-electric presses often come with built-in data monitoring systems. Unlike traditional hydraulic or pneumatic presses, servo presses precisely control force and position using programmable servo motors. These presses can monitor every aspect of the cycle natively and record highly detailed process data without the need for additional sensors.
Integrated monitoring is ideal for highly automated production lines and facilities using Industry 4.0 or SCADA systems. Built-in connectivity allows servo presses to feed real-time quality data directly into plant management software, making it easier to track production metrics, perform predictive maintenance, and maintain traceability for critical parts.
How to Match Monitoring Equipment to Your Application
Now that we’ve covered the different types of press monitoring equipment, how do you choose the right one for your operation? The answer depends largely on your application’s complexity, production volume, and quality requirements.
Applications for Basic Force Monitoring
If your process involves straightforward pressing tasks—such as inserting bushings, seating fasteners, or simple staking operations—basic force monitoring may be sufficient. These systems provide a low-cost safeguard against major process failures without introducing significant complexity into the line.
Applications for Force and Distance Monitoring
When working with parts that have strict dimensional tolerances or require multi-stage pressing operations, a combination of force and distance monitoring may be ideal. Applications like electronic connector assembly, sealed enclosures, and precision-fit mechanical parts benefit greatly from this additional layer of process control.
Applications for Signature Analysis
High-volume, high-precision industries such as automotive manufacturing, aerospace production, and medical device assembly often require signature monitoring. Signature analysis not only helps to prevent product defects, but also provides valuable diagnostic information that can help improve overall process stability and reliability over time.
Applications for Integrated Servo Monitoring
Facilities with fully-integrated smart manufacturing practices or those that produce highly regulated products (such as medical implants or advanced automotive & aerospace components) will often benefit most from presses with integrated servo monitoring. The ability to automatically record, store, and analyze pressing data makes compliance with regulatory requirements easier and allows for real-time process optimization.
How to Choose the Best Press Monitoring Equipment for Your Application
The best press monitoring system is the one that fits your production needs—not necessarily the one with the most features or highest price tag. As manufacturing demands continue to evolve, the ability to monitor, analyze, and optimize your pressing operations will only become more important. Investing in the right press monitoring equipment today can set you up for greater efficiency, higher quality, and long-term success tomorrow.
If you’d like help selecting the best monitoring solution for your presses, contact our team. We’re here to help you find the right fit for your application.